Adobe Flash Stickman Template
Flash is a multimedia platform which was developed by Macromedia company in 1996. Currently (since 2005) it distributed by Adobe Systems. Platform provide animation, audio and video streaming, interactive presentations. It is used for games, advertisements, websites. Content using Adobe Flash Player may be displayed on different operational systems and mobile devices. Adobe Flash Templates - are websites created by Adobe Flash program. It allow to build own flash based site, it makes it more interactive and expressive.
Using our flash templates your website can become more interesting to your visitors, they'll explore your site further. When using our Macromedia Flash 8 Templates there are no issues with cross browser compatibility, which means your multimedia elements will be exactly the same on all browsers. Adobe has taken animation to the next level - it's make your site cool. Most websites are boring and not appealing to the eyes - but with the use of our Macromedia Flash 8 Templates they can be transformed into elegant ones. In this category, you can see different types of templates. The most common is flash 8 template. Dynamic flash templates allows you to modify the content of the site without recompiling fla file.
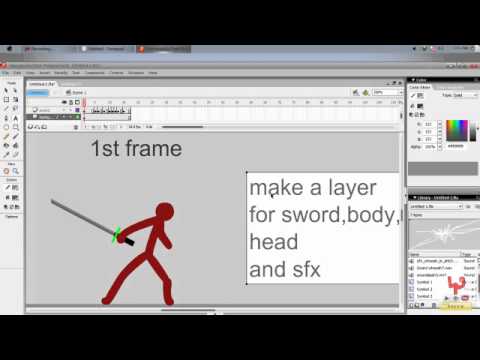
An all purpose animation of a stick man/stick figure walking (and getting hit by a big boulder).but there's a very good walking animation within the.fla file =D. Free flash animations made by various artists. Some of the flash animations require flash player 7 or later. Click the thumb image to preview the animation.
All information in this case are stored in a text file. Flash Photo and video galleries are templates made by dynamic technology with the additional admin panel for photo and video sections.
Flash intros are good choise for presentations or for your intro page. We provide wide range of products - so you'll certainly find what you're looking for.
Adobe Flash Stickman Download
Free download stickman template flash Files at Software Informer. Loved by game developers, students, cutout animators, artists, teachers, musicians, hobbyists.
The purpose of the Voluntary Product Accessibility Template is to assist Federal contracting officials in making preliminary assessments regarding the availability of commercial Electronic and Information Technology products and services with features that support accessibility. It is assumed that offerers will provide additional contact information to facilitate more detailed inquiries.
The first table of the Template provides a summary view of the section 508 Standards. The subsequent tables provide more detailed views of each subsection. There are three columns in each table. Column one of the Summary Table describes the subsections of subparts B and C of the Standards.
The second column describes the supporting features of the product or refers you to the corresponding detailed table, 'e.g., equivalent facilitation.' The third column contains any additional remarks and explanations regarding the product. In the subsequent tables, the first column contains the lettered paragraphs of the subsections. The second column describes the supporting features of the product with regard to that paragraph.
The third column contains any additional remarks and explanations regarding the product. Date: April 23, 2012 Name of product: Adobe ® Flash ® Professional CS6 Contact for more information. Summary Table Guideline Applicable Compliance Section 1194.21 Applicable Supports with exceptions Section 1194.22 Applicable Supports Section 1194.23 Telecommunications Products Not applicable — Section 1194.24 Applicable Supports Section 1194.25 Self-Contained, Closed Products Not applicable — Section 1194.26 Desktop and Portable Computers Not applicable — Section 1194.31 Applicable (Application) Applicable (Flash based content) Supports with exceptions Supports with exceptions Section 1194.41 Applicable Supports. Section 1194.21 Software Applications and Operating Systems — Detail Criteria Supporting features Remarks and explanations (a) When software is designed to run on a system that has a keyboard, product functions shall be executable from a keyboard where the function itself or the result of performing a function can be discerned textually. Supports with exceptions Customizable keyboard navigation or equivalent keyboard accessible controls are provided for all menu commands and most common features in Adobe Flash Professional CS6. However, some commands and functions are not usable from the keyboard alone including:.
Actions related to timeline manipulation, drawing and animation on the workspace are generally not keyboard accessible. However, scripting can be used to add and manipulate predefined objects on the stage. There is limited keyboard access to panels using the keyboard. For example, keyboard shortcuts can be used to place focus on the Properties panel but it is not possible to get to controls beyond the panel title and menu.
Focus has to be placed within the controls with a mouse first. Some controls in panels are not operable using a keyboard alone. For example, it is not possible to drag a component to the stage from the Component panel, using the keyboard alone. Expand/Collapse controls in the Properties panel are not operable using a keyboard. Some sections in dialog boxes, such as the General section in the Preferences dialog, do not have a logical tab order. Some controls in dialog boxes, such as the checkboxes in the formats list in the Publish Settings dialog, are not keyboard accessible.
(b) Applications shall not disrupt or disable activated features of other products that are identified as accessibility features, where those features are developed and documented according to industry standards. Applications also shall not disrupt or disable activated features of any operating system that are identified as accessibility features where the application programming interface for those accessibility features has been documented by the manufacturer of the operating system and is available to the product developer. Supports Flash Professional CS6 does not interfere with operating system accessibility features. (c) A well-defined on-screen indication of the current focus shall be provided that moves among interactive interface elements as the input focus changes. The focus shall be programmatically exposed so that Assistive Technology can track focus and focus changes.
Supports with exceptions There is a clear indication of focus for most focusable elements in the Flash Professional CS6 interface with minor exceptions, such as the Highlight Color radio buttons in the Preferences dialog box. In some cases focus is not programmatically exposed to assistive technology. For example, objects on the stage or controls in the File Info.
Dialog box do not provide focus information. (d) Sufficient information about a user interface element including the identity, operation, and state of the element shall be available to Assistive Technology. When an image represents a program element, the information conveyed by the image must also be available in text. Supports with exceptions Many controls and features of the Flash Professional CS6 interface provide identity, role, and state information to assistive technology with some exceptions including:. Controls in some dialog boxes, such as combo boxes in the Publish Settings dialog, do not include labels.
Some controls, such as Expand/Collapse controls do not include meaningful labels. Some controls in panels, such as outline items in the Components panel, do not include accessible name information. Objects on the stage do not provide sufficient information to assistive technology. (e) When bitmap images are used to identify controls, status indicators, or other programmatic elements, the meaning assigned to those images shall be consistent throughout an application's performance. Supports Bitmap images are used consistently in Flash Professional CS6. (f) Textual information shall be provided through operating system functions for displaying text.
The minimum information that shall be made available is text content, text input caret location, and text attributes. Supports with exceptions Textual information within the document being authored is not available to assistive technologies.
Some panels such as the code editor in the Actions panel, contain text that is not exposed through operating system functions for displaying text. (g) Applications shall not override user-selected contrast and color selections and other individual display attributes. Supports with exceptions Many controls in the Flash Professional CS6 interface support Windows High Contrast mode. However, most panels, such as the main workspace, Timeline and Properties panels do not properly inherit user defined high contrast schemes. Some dialog boxes, such as the Document Settings dialog, do not inherit user settings.
(h) When animation is displayed, the information shall be displayable in at least one non-animated presentation mode at the option of the user. Not applicable The Flash Professional CS6 interface does not use animation. (i) Color coding shall not be used as the only means of conveying information, indicating an action, prompting a response, or distinguishing a visual element. Supports The Flash Professional CS6 interface does not use color alone to convey information.
(j) When a product permits a user to adjust color and contrast settings, a variety of color selections capable of producing a range of contrast levels shall be provided. Not applicable Flash Professional CS6 does not allow users to change color and contrast settings. (k) Software shall not use flashing or blinking text, objects, or other elements having a flash or blink frequency greater than 2 Hz and lower than 55 Hz. Supports Flash Professional CS6 does not use flashing or blinking text in the user interface. (l) When electronic forms are used, the form shall allow people using Assistive Technology to access the information, field elements, and functionality required for completion and submission of the form, including all directions and cues.
Supports with exceptions Some form controls in panels are not reachable using a keyboard alone such as icon buttons in the Transform panel. Some form controls in panels, such as combo boxes in the Character panel, do not include labels. Some form controls in dialog boxes, such as color pickers in the Preferences and Document Settings dialogs, are not reachable using a keyboard alone. Controls in some dialog boxes, such as combo boxes in the Publish Settings dialog, do not include labels. Some controls, such as Expand/Collapse controls do not include meaningful labels. Section 1194.22 Web-based Intranet and Internet Information and Applications — Detail Criteria Supporting features Remarks and explanations (a) A text equivalent for every non-text element shall be provided (e.g., via 'alt,' 'longdesc,' or in element content).

Supports Flash Professional CS6 allows authors to assign test alternatives to non-text elements using the Accessibility panel or ActionScript properties. (b) Equivalent alternatives for any multimedia presentation shall be synchronized with the presentation. Supports Flash Professional CS6 provides a captioning component that enables the addition of captions to video presentations. It also allows audio descriptions to be implemented for multimedia presentations. (c) Web pages shall be designed so that all information conveyed with color is also available without color, for example from context or markup. Supports Flash Professional CS6 allows authors to convey meaning with alternatives or with additional text. (d) Documents shall be organized so they are readable without requiring an associated style sheet.
Not applicable Flash based content does not rely on CSS for rendering. (e) Redundant text links shall be provided for each active region of a server-side image map. Not applicable Flash based content does not contain server-side image maps. (f) Client-side image maps shall be provided instead of server-side image maps except where the regions cannot be defined with an available geometric shape. Not applicable Flash based content does not contain client-side image maps. (g) Row and column headers shall be identified for data tables.
Supports The DataGrid component combines column header names with cell values as pairs. (h) Markup shall be used to associate data cells and header cells for data tables that have two or more logical levels of row or column headers. Not applicable The Flash Professional CS6 DataGrid does not provide multiple/nested table headers. If authors create a component with multiple rows of header cells, this information should be combined with the accessible name of the associated row or cell (list item). Flash does not provide components that use the accessible roles of header cell or data cell. (i) Frames shall be titled with text that facilitates frame identification and navigation. Not applicable Flash content does not contain frames.

(j) Pages shall be designed to avoid causing the screen to flicker with a frequency greater than 2 Hz and lower than 55 Hz. Supports Flash Professional CS6 allows content to be generated that does not contain flickering elements, or flickering within safe frequencies. (k) A text-only page, with equivalent information or functionality, shall be provided to make a web site comply with the provisions of this part, when compliance cannot be accomplished in any other way. The content of the text-only page shall be updated whenever the primary page changes.
Supports Flash authors can create a text only version of their content. (l) When pages utilize scripting languages to display content, or to create interface elements, the information provided by the script shall be identified with functional text that can be read by Assistive Technology. Supports The ActionScript language allows accessible content and interface elements to be generated that are available to assistive technology. (m) When a web page requires that an applet, plug-in, or other application be present on the client system to interpret page content, the page must provide a link to a plug-in or applet that complies with §1194.21(a) through (l). Supports A plug-in for the Adobe Flash Player is available on the Adobe website.
If the plug-in is not installed the user will be presented with a download link or the author can provide a link where they use the Flash content. (n) When electronic forms are designed to be completed on-line, the form shall allow people using Assistive Technology to access the information, field elements, and functionality required for completion and submission of the form, including all directions and cues. Supports Flash Professional CS6 allows authors to assign accessible names and descriptions to form controls to provide information to assistive technology users. For built-in controls, keyboard accessibility is provided. For custom controls, authors can manually assign key events to achieve this.
(o) A method shall be provided that permits users to skip repetitive navigation links. Supports Flash Professional CS6 allows authors to add interactive controls and shortcuts to move keyboard focus past repetitive navigation links. (p) When a timed response is required, the user shall be alerted and given sufficient time to indicate more time is required. Supports Flash Professional CS6 allows authors to use alert boxes to enable users to confirm more time is required. Section 1194.24 Video and Multimedia Products — Detail Criteria Supporting features Remarks and explanations a) All analog television displays 13 inches and larger, and computer equipment that includes analog television receiver or display circuitry, shall be equipped with caption decoder circuitry which appropriately receives, decodes, and displays closed captions from broadcast, cable, videotape, and DVD signals. As soon as practicable, but not later than July 1, 2002, widescreen digital television (DTV) displays measuring at least 7.8 inches vertically, DTV sets with conventional displays measuring at least 13 inches vertically, and stand-alone DTV tuners, whether or not they are marketed with display screens, and computer equipment that includes DTV receiver or display circuitry, shall be equipped with caption decoder circuitry which appropriately receives, decodes, and displays closed captions from broadcast, cable, videotape, and DVD signals. Not applicable Flash Professional CS6 content does not include hardware components.
(b) Television tuners, including tuner cards for use in computers, shall be equipped with secondary audio program playback circuitry. Not applicable Flash Professional CS6 does not include any television tuner hardware. (c) All training and informational video and multimedia productions which support the agency's mission, regardless of format, that contain speech or other audio information necessary for the comprehension of the content, shall be open or closed captioned. Supports Flash Professional CS6 provides a captioning component that enables authors to add closed captions to multimedia presentations. (d) All training and informational video and multimedia productions which support the agency's mission, regardless of format, that contain visual information necessary for the comprehension of the content, shall be audio described. Supports Flash Professional CS6 allows authors to provide audio descriptions in multimedia presentations through scripting.
Stickman Flash Games
(e) Display or presentation of alternate text presentation or audio descriptions shall be user-selectable unless permanent. Supports Caption text can be turned on or off by the user. Section 1194.31 Functional Performance Criteria — Detail Criteria Supporting features Remarks and explanations (a) At least one mode of operation and information retrieval that does not require user vision shall be provided, or support for Assistive Technology used by people who are blind or visually impaired shall be provided. Does not support (Application) Supports with exceptions (Flash based output) Most actions in Flash Professional CS6 related to timeline editing and content editing cannot be performed with a screen reader.
Some controls in dialog boxes and panels do not provide sufficient information to assistive technologies. Many controls in panels are not reachable using a keyboard alone. Flash based Output: Form controls can be made accessible for screen readers.
Some events used by assistive technology are not fired by default in the combo box. The text of an editable combo box cannot be reviewed character by character via a screen reader. The roles of the numeric stepper, slider, and color picker are not indicated to users of screen readers.
DataGrids that are editable are difficult to navigate via the keyboard by default. Authors are able to extend and customize the DataGrid component to improve the keyboard access. (b) At least one mode of operation and information retrieval that does not require visual acuity greater than 20/70 shall be provided in audio and enlarged print output working together or independently, or support for Assistive Technology used by people who are visually impaired shall be provided. Supports with exceptions (Application) Supports (Flash based content) Flash Professional CS6 supports the use of Screen Magnifiers. However, in some cases there is not a clear visual indication of focus and focus is not programmatically exposed to assistive technology.
Flash Professional CS6 has limited support for Windows High Contrast mode. Flash based Output: All elements in Flash based content can be made focusable and can provide a visual indication of focus. Although Flash content does not inherit color and contrast settings specified by the operating system, the Flash author can provide such color schemes manually. (c) At least one mode of operation and information retrieval that does not require user hearing shall be provided, or support for Assistive Technology used by people who are deaf or hard of hearing shall be provided. Supports (Application) Supports (Flash based content) Flash Professional CS6 does not require hearing for operation. Flash based Output: Flash Professional CS6 allows caption files to be added to Flash multimedia content. For content that uses auditory cues, the Flash author can provide visual cues manually.
(d) Where audio information is important for the use of a product, at least one mode of operation and information retrieval shall be provided in an enhanced auditory fashion, or support for assistive hearing devices shall be provided. Supports (Application) Supports (Flash based content) Flash Professional CS6 does not require hearing for operation. Flash based Output: Flash Professional CS6 allows caption files to be added to Flash multimedia content.
For content that uses auditory cues, the Flash author can provide visual cues manually. (e) At least one mode of operation and information retrieval that does not require user speech shall be provided, or support for Assistive Technology used by people with disabilities shall be provided. Supports (Application) Supports (Flash based content) Flash Professional CS6 does not require user speech. Flash based Output: Flash content can be created that does not require user speech.
(f) At least one mode of operation and information retrieval that does not require fine motor control or simultaneous actions and that is operable with limited reach and strength shall be provided. Does not support (Application) Supports (Flash based content) Flash Professional CS6 supports accessibility features of the operating system such as Sticky Keys, which may be used during some editing operations that may require the use of keyboard modifiers and mouse selections. However some operations, such as expanding and collapsing sections in the Properties panel, may require fine motor control and there is no keyboard equivalent.
Some editing operations on the stage, such as constraining selections and drawing objects require simultaneous mouse and keyboard actions. Flash based Output: Flash provides built-in controls that are keyboard accessible, and allow authors to manually implement keyboard support for custom controls. Section 1194.41 Information, Documentation, and Support — Detail Criteria Supporting features Remarks and explanations (a) Product support documentation provided to end-users shall be made available in alternate formats upon request, at no additional charge. Supports Adobe provides electronic versions of all product support documentation.
(b) End-users shall have access to a description of the accessibility and compatibility features of products in alternate formats or alternate methods upon request, at no additional charge. Supports Adobe provides information on accessibility features in the documentation. Electronic versions of all product support documentation are provided.
(c) Support services for products shall accommodate the communication needs of end-users with disabilities. Supports Product support for Adobe products is available in a variety of formats and from a number of online sources available from Adobe Systems.
Comments are closed.